Programming extension roadmap
- Getting started
- 2 dimensional arrays
- Recursion
- Graph theory & Depth first search (matrices)
- Breadth first search (matrices)
- Check-in point
- Diploma CS topics that are useful to know
- Topics for further investigation
The extension roadmap assumes you are already confident in the core skills of IGCSE programming.
As you work through these extension tasks please regularly save your progress into the github repo. This will help me monitor your progress - check for your understanding, see if you are getting stuck, and monitor pacing (when do I have to add additional items to this doc).
Getting started
These are problems using the programming skills from the course, but are slightly more challenging with respect to the problem solving skill required.
-
Solve: Engine diagnostics https://codingquest.io/problem/1 Processing a 1D array to perform calculations Tip: Ask me to explain the phrase “moving average” if it is unfamiliar to you
-
Solve: Lottery tickets https://codingquest.io/problem/2 You’ll be given a long file, each line of the file contains a 1D array of 6 numbers. Perform calculations on the numbers in each line.
-
Solve: Tour the stars https://codingquest.io/problem/3 You’ll be given a long file, each line of the file contains a set of numbers representing coordinates in a 3D space. It’s effectively Pythagoras in 3 dimensions.
-
Solve: Wordle with friends https://codingquest.io/problem/14 This is a problem that requires you to use your strings functions. If you are familiar with Wordle, you can probably manually solve this without programming it, but I recommend going through the process of creating the program anyway to practice your strings functions. .
-
Solve: Snakes & ladders https://codingquest.io/problem/13 This question presents the classic snakes and ladders game, and appears as a 2D array. While you can solve it as that, the trick to making it “easy” is to realise that playing the “game” is a lot easier if you convert the 2D array into a 1D array first, and walk forward and backwards over the 1D array. If that doesn’t make sense, try watching the video or asking me what I mean. If you are struggling and would like a walkthrough, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7OAWyI3Q15s
2 dimensional arrays
-
Solve: Average rows & columns Given two dimensional data in the following form, calculate the average mark for each student, and the average mark for each test.
-
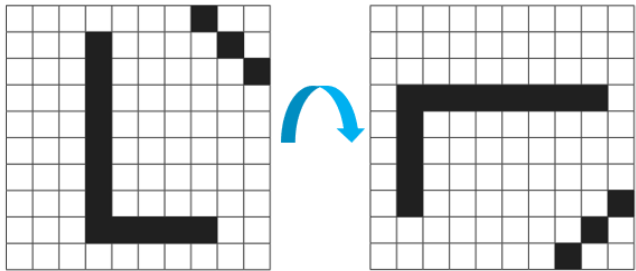
Solve: Rotate an image Two dimensional arrays can be used to represent images in apps like Photoshop. Create a program that will perform a 90 degree rotation on data such as follows:
- Solve: Downsample an image Two dimensional arrays can be used to represent images in apps like Photoshop. Create a program that will resize an image from 10x10 pixels to either 5x5 or 2x2 pixels.
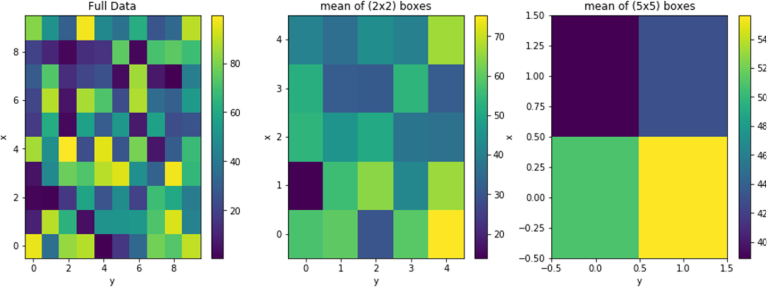
For this input data…
original = [
[ 255, 102, 87, 196, 96, 91, 163, 132, 91, 225 ],
[ 80, 74, 63, 77, 77, 255, 64, 255, 255, 228 ],
[ 86, 255, 73, 81, 83, 64, 252, 69, 58, 95 ],
[ 82, 221, 70, 228, 255, 83, 82, 241, 91, 124 ],
[ 80, 176, 62, 146, 88, 117, 72, 143, 82, 84 ],
[ 246, 99, 210, 85, 187, 85, 255, 65, 85, 215 ],
[ 65, 96, 255, 255, 220, 189, 102, 88, 204, 208 ],
[ 61, 58, 81, 146, 85, 98, 81, 231, 169, 94 ],
[ 73, 221, 195, 66, 109, 111, 117, 255, 190, 97 ],
[ 191, 91, 241, 230, 59, 244, 89, 240, 255, 218 ],
]
Answers would be (numbers given as decimal)
Recursion
Recursion & memorisation in Python
Create the fibonacci sequence program - Test for yourself the difference between using memorisation and not. Can you understand why memorisation is needed / what it is doing?
Create a program that calculates factorials
Attempt 4 or 5 of the recursion-1 set on codingbat, https://codingbat.com/java/Recursion-1 Note: This platform is designed for Java, so you won’t be able to use their systeem for testing/submitting answers. Just save your code to your github repo for me to see.
Attempt 3+ of the recursion questions here, https://www.w3resource.com/c-programming-exercises/recursion/index.php
Solve: Mergesort
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4VqmGXwpLqc
- https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Su3s0GQFw2YCC2yDXSucxmmChYbAjobc/view?usp=sharing
- Test your merge sort on this file containing 10000 unsorted numbers.
Solve: Quicksort
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hoixgm4-P4M
- https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Su3s0GQFw2YCC2yDXSucxmmChYbAjobc/view?usp=sharing
- Test your quick sort on this file containing 10000 unsorted numbers.
Learn: Towers of Hanoi: A Complete Recursive Visualization
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rf6uf3jNjbo (21:12, Reducible)
Graph theory & Depth first search (matrices)
Learn: Introduction to Graph Theory: A Computer Science Perspective
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LFKZLXVO-Dg (16:25, Reducible)
Learn: Depth First Search (DFS) Explained: Algorithm, Examples, and Code
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PMMc4VsIacU (20:51, Reducible)
Solve: Survey an asteroid belt
- https://codingquest.io/problem/15 - A good test of 2D arrays, recursion and depth first search. If you get stuck, watch some of the walk through video (I recommend only watching what you need and solving as much as you can without it)… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dw4jsbPCNpA
Breadth first search (matrices)
Learn: Breadth First Search (BFS): Visualized and Explained (10:40, Reducible)
Solve: Lost in an alien market
Maze solving problem: At first glance you may think Depth First Search could work on this, and if the maze was a little smaller it probably would. The reality is the size of the problem is too much for recursion to cope on most modern computers and an alternative method is required. Learn about the use of stacks in breadth first search.
Solve: Wormholes in space
Check-in point
Congratulations, you’ve achieved a lot!
You are now at the point it is worth you and I having a conversation about next steps, and putting together a pathway that is more tailored for you personally. There are a lot of different directions we can head from here, and it isn’t necessarily just a linear track anymore. Let’s have a chat!
Diploma CS topics that are useful to know
Object oriented programming
- Requires: Datatypes, Functions
- Big ideas: Defining datatypes, Instantiation, Dependencies, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism
- Read chapter B3 Object oriented programming, Computer Science for the IB Diploma
Key concepts you want to grasp from this (it is worth us having a discussion to ensure understanding)
- Classes and objects
- Constructor & Instantiation
- Access modifiers and encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
Linked Lists
- Requires: OOP, Recursion
- Big ideas: Node based data structures, dynamically sized data structures
- Example problems: traversal / insertion / deletion within the chain
- Watch: CS50 (2020) - Lecture 5 - Data Structures (note: the lecture starts at 11:10). This lecture will be important for linked lists, stacks, queues and binary trees.
Solve: https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
Stacks & Queues
Requires: Linked lists
Big ideas: First in, first out; First in, last out
Solve: https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-parentheses/ https://leetcode.com/problems/baseball-game/
Binary trees
Requires: Linked lists
Big ideas: Binary trees
Example problems: Binary search tree, Huffman encoding
Solve:
- Subordinates - https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1674
- Tree Diameter - https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1131
- Distance queries - https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1135
Topics for further investigation
The following is a list of topics we can discuss for the future. I do have an assorted array of resources / books / exercises for these that I can supply.
-
Build your own neural network Big ideas: Matrices, network layers, training Example problems: Build your own NN; Object detection & recognition; CCTV cameras/tracking, natural language processing, language translation
-
Path finding Big ideas: Dikstra, A star Requires: Graph traversal Example problem: Maze solving, shortest path finding
-
Compression Requires: Binary trees Big idea: Huffman encoding
-
Genetic algorithms Example problems: Travelling salesman
-
Reinforcement learning Big idea: Q-learning Example problems: Training a bot to play a computer game
-
Networking Big ideas: Protocols, addressing, OSI layers, writing using APIs Project ideas: Create your own firewall, ad blocker, DNS server, proxy server, etc
-
Systems programming Big ideas: Operating systems, CPU architecture & instruction set, interrupts, memory management - stack vs heap, linking, libraries, i/o, drivers, multi core/processor parallel programming Examples: Assembler, C, Create your own programming language, compiler
-
Physical computing Big ideas: Digital to analogue signal conversions, voltages/currents/electronics Examples: Arduino’s, Raspberry Pi’s, Robotics, Drones, etc
-
Cryptography Big ideas: Symmetric, asymmetric, hash algorithms, certificate signing Example: Create your own blockchain
-
Game design Animation, Modelling, Rendering Visualisation, 3D spaces, Physics systems, VR world building