B2 Programming
For the new IB Diploma Computer Science syllabus to start teaching in August 2025, and for first examinations in May 2027.
Unit and lesson overviews will be gradually published as developed.
- Teaching slides
- Lesson 1: Hello world
- Lesson 2-9: IGCSE programming recap
- Lesson 10: Exception handling & debugging techniques
- Lesson 11: Stacks
- Lesson 12: Queues
- Lesson 13: Big O
- Lesson 14,15: Search algorithms
- Lesson 16,17: Sort algorithms
- Lesson 18,19,20: Recursion (HL)
- Lesson 21: File processing
- Lesson 22-27: Programming scenarios
- Lesson 28,29: Review
- Lesson 30: Assessment
Teaching slides
- Unit B2 teaching slides (access to my students only)
Lesson 1: Hello world
- Install VS Code
- Install Github Desktop
- Create a Github account
- Create a Github repo
- Add me as a collaborator
- Practice uploading to your Github repo
- Checking the automated testing
Using Hackerank and Leetcode
- Solve Me First (Function, arithmetic)
Lesson 2-9: IGCSE programming recap
- B2.1.1 Construct and trace programs using a range of global and local variables of various data types.
- B2.1.2 Construct programs that can extract and manipulate substrings.
- B2.2.2 Construct programs that apply arrays and Lists.
- B2.3.1 Construct programs that implement the correct sequence of code instructions to meet program objectives.
- B2.3.2 Construct programs utilizing appropriate selection structures.
- B2.3.3 Construct programs that utilize looping structures to perform repeated actions.
- B2.3.4 Construct functions and modularization.
Lesson 2 through 9 are a quick recap of programming skills from IGCSE Computer Science. Those confident with their IGCSE programming can do a mini project to refresh their Python and demonstrate their competency with these skills in lieu of the exercises in these lessons.
B2 problem set 1 draws on all the programming skills from IGCSE.
If you need to revisit the original IGCSE programming exercises, they are here: IGCSE Programming 1 problem set
Exercise 1: Temperature Tracker
Given a file containing daily temperature readings (one per line), calculate:
- The average temperature.
- The highest and lowest temperatures.
- The number of days when the temperature increased compared to the previous day.
Input:
Function name:
temerature_tracker()
Return 4 integers:
- Average temperature, rounded to nearest integer
- Highest temperature, rounded to nearest integer
- Lowest temperature, rounded to nearest integer
- Number of days when the temperature increased compared to the previous day
Exercise 2: Spell checker
Given a text document (mystery.txt) and a dictionary of valid words, determine how many words in the mystery document have been spelt correctly. Ignore casing and punctuation.
Input:
- mystery-text.txt (story generated by LLM)
- dictionary.txt
Function name:
spell_check()
Return value:
- Return an integer being the number of correctly spelt words.
Exercise 3: Maze Navigator
Read a text file representing a grid (2D list) where:
.is open space#is a wallSis the startEis the end
Write a program to find the shortest path from S to E using only up/down/left/right moves. Note: If you know recursion, avoid using it, just simulate movement with loops.
Input:
Function name:
maze_navigator()
Return value:
- An integer, being the number of steps taken to solve the maze (the starting location is 0, and you must step into the end location).
Exercise 4: Frequency Counter
Read a list of words and count how many times each word appears. Return a list of results being the same list of words in descending order of frequency. (Ignoring case and punctuation)
Input:
Function name:
frequency_counter()
Return value:
- A list of strings, being the words in descending order of frequency.
Exercise 5: Robot Instructions
A robot starts at position (0, 0) on a 2D grid. A file contains instructions like:
UP 5
LEFT 3
DOWN 2
RIGHT 4
Determine the robot’s final position and total distance traveled.
Input:
Function name:
robot_instructions()
Return value:
- Three values, being the
Xcoordinate,Ycoordinate, andTOTAL_DISTANCE_TRAVELLED
Additional exercises
Leetcoode problems
- #1 - Two Sum (Nested loops, lists)
- #412 - Fizz Buzz (Conditionals, loops)
- #9 - Palindrome Number (Integer/str conversion)
- #125 - Valid Palindrome (String cleaning)
- #88 - Merge Sorted Arrays (Lists, loops)
- #26 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array (List processing)
- #38 - Count and Say (String processing)
Hackerrank problems
- Simple Array Sum (Loops, summing values)
- Compare the Triplets (Lists, conditionals)
- A Very Big Sum (Large number handling)
- Diagonal Difference (2D lists)
- Plus Minus (Counting, floats)
- Staircase (patterns, printing)
- Mini-Max Sum (Sorting, arithmetic)
- Birthday Cake Candles (Max value counting)
Lesson 10: Exception handling & debugging techniques
Lesson 10 onwards comprises of post-IGCSE content
- B2.1.3 Describe how programs use common exception handling techniques.
- B2.1.4 Construct and use common debugging techniques.
Exercise 1: Student grades calculator
The following program reads a list of students and their grades from a file, calculates their average, and prints a report. The file may have missing, non-numeric, or corrupt data. You must handle exceptions and debug logic errors.
- Add breakpoints or print statements to inspect grade_list
- Use a trace table to follow data for each student
- Step through error cases and fix input validation
def read_grades(filename):
with open(filename) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
name, *grades = line.strip().split(',')
grade_list = [int(g) for g in grades] # May raise ValueError
avg = sum(grade_list) / len(grade_list) # May raise ZeroDivisionError
print(f"{name} - Average: {avg:.2f}")
try:
read_grades("grades.csv")
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File not found. Please check the filename.")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Invalid grade value: {e}")
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("No grades found for a student.")
finally:
print("Grade processing completed.")
Sample CSV data
Alice,85,90,92
Bob,80,abc,77
Charlie,
Daisy,100,95
Exercise 2: Simple ATM Simulator
Create a basic ATM program that allows a user to withdraw money. The program should prompt the user for withdrawal amount, and raise exceptions for:
- Invalid inputs (non-numeric)
- Overdrafts (withdrawal > balance)
- Unavailable resources (simulate ATM out of cash)
- Include finally block to close session/log out
Solve through:
- Set breakpoints on input and condition checks
- Use step-by-step debugging to trace variable states
- Add a trace table for inputs: 200, 600, 1200, ‘abc’
def withdraw(balance):
amount = int(input("Enter amount to withdraw: ")) # May raise ValueError
if amount > balance:
raise Exception("Insufficient funds.")
if amount > 1000:
raise Exception("ATM is out of cash.")
balance -= amount
print(f"Withdrawn: {amount}. Remaining balance: {balance}")
return balance
balance = 500
try:
balance = withdraw(balance)
except ValueError:
print("Please enter a valid number.")
except Exception as e:
print("Transaction error:", e)
finally:
print("Transaction session ended.")
(thanks to LLM for these two exercises)
Lesson 11: Stacks
- B2.2.1 Compare static and dynamic data structures.
- B2.2.3 Explain the concept of a stack as a “last in, first out” (LIFO) data structure.
Exercises
- Leetcode 20 Valid Parentheses
- Leetcode 155 Min stack
- Hackerrank Balanced brackets
- Advent of code 2021 day 10 Syntax Scoring
Lesson 12: Queues
- B2.2.4 Explain the concept of a queue as a “first in, first out” (FIFO) data structure.
Exercises
- Leetcode 1700 Number of students unable to eat lunch
- Hackrank Queue using Two Stacks
- Advent of code 2019 Day 5 part 1 Sunny with a Chance of Asteroids
Lesson 13: Big O
- B2.4.1 Describe the efficiency of specific algorithms by calculating their Big O notation to analyse their scalability.
Lesson 14,15: Search algorithms
- B2.4.2 Construct and trace algorithms to implement a linear search and a binary search for data retrieval.
Exercises
- Leetcode 704 Binary search
- Hackerrank Ice Cream Parlor
- Leetcode 35 Search insert position
Lesson 16,17: Sort algorithms
- B2.4.3 Construct and trace algorithms to implement bubble sort and selection sort, evaluating their time and space complexities.
Exercises
- Hackerrank 30 days of code Day 20: Sorting
- Leetcode 75 Sort Colors
- Leetcode 88 Merge sorted array
- Advent of code 2020 day 5 Binary Boarding
Lesson 18,19,20: Recursion (HL)
- B2.4.4 Explain the fundamental concept of recursion and its applications in programming. (HL only)
- B2.4.5 Construct and trace recursive algorithms in a programming language. (HL only)
Exercises
- Hackerrank 30 days of code Day 9 Recursion 3
- Leetcode 509 Fibonacci number
- Leetcode 704 Binary search - Implement a recursive solution to binary search
- Hackerrank Recursive Digit Sum - Recursively calculate the sum of all the digits in a number
- Leetcode 9 Palindrome Number - Recursively determine if a number is a palindrome
- Leetcode 1979 Find Greatest Common Divisor of Array - Recursively calculate the greatest common divisor of two numbers. Note: This relies on the mathematical principle that GCD(a,b)=GCD(b, a mod b)
- Advent of code 2019, day 6 Universal Orbit Map
- Leetcode 733 Flood fill (DFS)
- Leetcode 695 Max area of Island (DFS)
Exercise: Quicksort
The Quicksort algorithm is specifically part of your syllabus so ensure you practice it!
Exercise: Sudoku
Sudoku is a puzzle game with numbers aligned in a 2D grid (perfect for a 2D array!). Some numbers are “given” and some cells are left blank for the problem solver to find. The aim of the puzzle is the fill in the blanks with numbers such that the same number can not appear more than once in any row or column. It is a puzzle that can be solved recursively.
Use recursive backtracking to solve the following Sudoku puzzle. The Python 2D list is given to you for copy-and-paste.
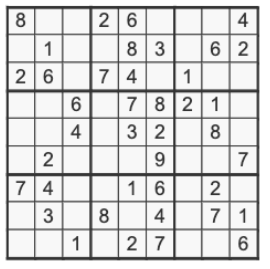
sudoku = [
[ 8, 0, 0, 2, 6, 0, 0, 0, 4 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 3, 0, 6, 2 ],
[ 2, 6, 0, 7, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 6, 0, 7, 8, 2, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 4, 0, 3, 2, 0, 8, 0 ],
[ 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 7 ],
[ 7, 4, 0, 0, 1, 6, 0, 2, 0 ],
[ 0, 3, 0, 8, 0, 4, 0, 7, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 7, 0, 0, 6 ]
]
The correct answer will be:
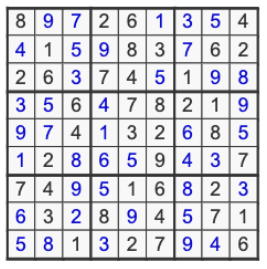
Lesson 21: File processing
- B2.5.1 Construct code to perform file-processing operations.
Exercises
- Advent of code 2021, day 1 Sonar sweep
- Advent of code 2022, day 1 Calorie counting
Lesson 22-27: Programming scenarios
Continue completing remaining problems from above. Work on the following additional problems as time allows:
- coming soon
Lesson 28,29: Review
Exam-style review