Tkinter GUI
Contents
- Starting a basic app
- Label, entry box and button
- Listbox and simpledialog
- Menubar and filedialog
- Images
- Second window
- Tabs
- Reference
- Assorted tips and tricks
- Suggested resources
Videos
- Video: A quick intro to Tkinter and object orientated programming
- Video: Using buttons in Tkinter
- Video: Using entry textbox in Tkinter
Reference
Creating a window
Imports
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
Template code to create a Tkinter window class.
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.parent = parent # Save a reference to our parent object
self.window = tk.Toplevel() # Create a window
self.window.geometry("400x200") # Set pixel dimensions 400 wide by 200 high
self.window.title("Test app") # Set window title text
self.window.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", self.window.quit) # Enable the close icon
# Add all your widgets here...
Main code to run the program
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk() # Initialise the tk system into an object called `root`
root.withdraw() # Hide the default window
app = AppWindow(root) # Run our window, called AppWindow
root.mainloop() # Start the program loop until all windows exit
To execute a function (in this case, self.window.quit()) when the window close icon is clicked
self.window.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", self.window.quit)
To make the window partially transparent
self.window.attributes('-alpha', 0.8)
To force the window to stay visibly on top of all other programs
root = tk.Tk()
root.wm_attributes("-topmost", 1)
To open a second window
# Create login window
login_window = LoginWindow()
# Wait until the login window is closed
self.window.wait_window(login_window.window)
print("Finished waiting")
# Execute a function on the login window object to retrieve data entered
data = login_window.get_data_entered()
To close a window, leaving the program (and any underlying window) running
self.window.destroy()
To close your entire program
self.window.quit()
Label
- Creating a label
self.hello_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Hello world!", font=FONT_LARGE)
self.hello_label.place(x=20, y=20)
- Set style parameters (color, font, etc)
self.image_label.place(x=20,y=70,width=300,height=300) # in pixels
- Set/change the text on a label
self.hello_label["text"] = "My new text"
- Styling a label
self.hello_label["font"] = ("Arial", 16)
self.hello_label["background"] = (255,255,0) # Yellow
self.hello_label["foreground"] = (128,128,128) # Grey
In order to fill a label with an image, see the Image section.
Text (Entry) box
Creating a text entry box
self.name_entry = tk.Entry(self.window)
self.name_entry.place(x=20, y=50)
To put the cursor in the text box
self.name_entry.focus() # Put the cursor in the text box
Get the text content of the entry box
person = self.name_entry.get()
Set/change the text value
self.name_text.delete(0, tk.END)
self.name_text.insert(0, contact["name"])
Set style and formatting parameters (color, font, etc)
self.name_text["state"] = "disabled" # set to "normal" to re-enable
self.name_text["font"] = ("Arial", 16)
self.name_text["background"] = (255,255,0) # Yellow
self.name_text["foreground"] = (128,128,128) # Grey
self.name_text["width"] = 20 # Width in number of characters. Does not limit number that can be typed
Mask the user input for use as a password entry box
self.widget = Entry(parent, show="*", width=15) # Show **** instead of the text entered
Button
Creating a button
# Set to execute self.greetings() when clicked...
self.submit_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Submit", command=self.greetings)
self.submit_button.place(x=20, y=100)
Set style parameters (color, font, etc)
self.button["text"] = "New description"
self.name_text["state"] = "disabled" # set to "normal" to re-enable
self.name_text["font"] = ("Arial", 16)
self.name_text["background"] = (255,255,0) # Yellow
self.name_text["foreground"] = (128,128,128) # Grey
self.name_text["width"] = 20 # Width in number of characters. Does not limit number that can be typed
To pass parameters along to the execute command use a lambda function
# Set to execute self.greetings() when clicked...
self.submit_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Submit", command=lambda: self.greetings(some_data))
self.submit_button.place(x=20, y=100)
# The corresponding function call header would then look like...
def greetings(self, data):
Listbox
Creating a listbox
# Create a list box
# -- width is characters, height is lines
self.list = tk.Listbox(self.window, width=10, height=10)
self.list.place(x=20, y=20)
# Add items into your list box
for item in items:
self.list.insert(tk.END, item) # Add each item to the end of the list
# -- Give `selected` a default of -1
self.selected = -1
Add item to list
self.list.insert(0, answer)
self.list.insert(tk.END, answer)
Delete item from list
self.list.delete(self.selected)
# Empty everything from the list
self.list.delete(0, tk.END)
Get number of items in list
count = self.list.size()
Get currently selected item in list
if len(self.list.curselection()) > 0: # If an item is selected
self.selected = int(self.list.curselection()[0]) # index number of selected item
item = self.list.get(self.selected) # text of selected item
Set currently selected item in list
self.listbox.select_set(0) # This sets focus on the first item.
self.listbox.event_generate("<<ListboxSelect>>")
Execute a function when selection changed
# -- When an item in the list is selected, execute the list_clicked function
self.list.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', self.list_clicked)
def list_clicked(self, e): # requires the 2nd parameter even though it doesn't tell you anything useful
print("You clicked on the list")
Menu
- Create a menu
# Create a menu bar
menubar = tk.Menu(self.window)
# Create a sub menu
filemenu = tk.Menu(menubar, tearoff=0)
filemenu.add_command(label="Open file", command=self.file_open)
filemenu.add_command(label="Save file as", command=self.file_saveas)
filemenu.add_command(label="Set default folder", command=self.select_folder)
filemenu.add_separator()
filemenu.add_command(label="Exit", command=self.window.quit)
# Create a sub menu
helpmenu = tk.Menu(menubar, tearoff=0)
helpmenu.add_command(label="About", command=self.about)
# Link the sub menus to the menu bar
menubar.add_cascade(label="File", menu=filemenu)
menubar.add_cascade(label="Help", menu=helpmenu)
# Set menu to the window
self.window.config(menu=menubar)
Tab
- Create a tab system
# Create tab containers & notebook
self.tab_container = tk.Frame(self.window)
self.tab_container.place(x=0,y=0,width=400,height=400)
self.tabs = ttk.Notebook(self.tab_container)
self.tabs.place(x=0,y=0,height=400,width=400)
# Create 3 tabs and add them to the notebook
self.tab_1 = tk.Frame(self.tabs)
self.tab_2 = tk.Frame(self.tabs)
self.tab_3 = tk.Frame(self.tabs)
self.tabs.add(self.tab_1, text="Tab 1")
self.tabs.add(self.tab_2, text="Tab 2")
self.tabs.add(self.tab_3, text="Tab 3")
# Define what function to run when current tab is changed
self.tabs.bind("<<NotebookTabChanged>>", self.on_tab_selected)
Add content to a tab
# Use the tab object as the first parameter of your widgets instead of the window
self.label1 = tk.Label(self.tab_1, text="I am the content of tab 1")
# Coordinates are relative to within the tab area
self.label1.place(x=20, y=20)
Image
Add an image to a label
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
# Open as a PIL image
img = Image.open(filename)
# 1. Convert the image into tk compatible form, and
# 2. Save a copy of the image to self otherwise it will be cleared from memory when this function closes
self.tkimg = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
# Display the image in the label
self.image_label.configure(image=self.tkimg)
Message box
from tkinter import messagebox
messagebox.showinfo("Greetings", f"Hello {person}, welcome to Tkinter!")
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Can't delete the selected item if you haven't selected anything!")
Simple Dialog box
from tkinter import simpledialog
answer = simpledialog.askstring("Title","Please type a string...")
answer = simpledialog.askinteger("Title","Please type an integer...")
answer = simpledialog.askfloat("Title","Please type a float...")
File Dialog box
from tkinter import filedialog
There are different dialogs available for file open, file save as, and choose folder.
ALLOWED_FILES = (("JPEG files","*.jpg"),("PNG files","*.png"),("all files","*.*"))
filename = filedialog.askopenfilename(title="Select file", filetypes=ALLOWED_FILES)
filename = filedialog.askopenfilename(initialdir=self.default_folder, title="Select file", filetypes=ALLOWED_FILES)
filename = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(initialdir=self.default_folder, title="Select file", filetypes=ALLOWED_FILES)
folder = filedialog.askdirectory(initialdir=self.default_folder, title = "Select folder containing student photos")
Examples
Example 1: A basic app
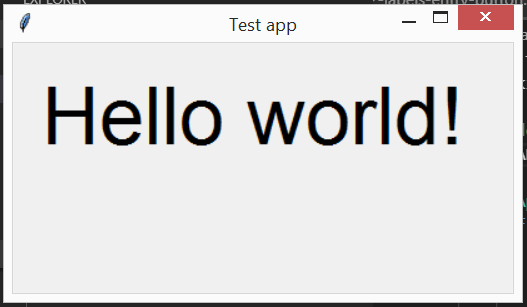
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# Pre-define some defaults
FONT_LARGE = ("Arial", 48)
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x200")
self.window.title("Test app")
self.window.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", self.window.quit) # Enable the close icon
# Create a text label and place it in the window
self.hello_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Hello world!", font=FONT_LARGE)
self.hello_label.place(x=20, y=20)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Example 2: Labels, entry box, button
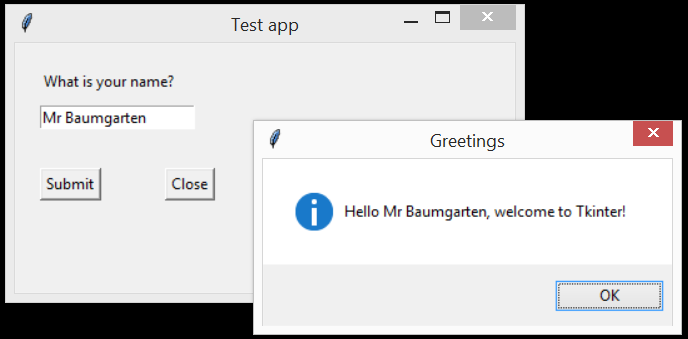
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import messagebox
# Pre-define some defaults
FONT_LARGE = ("Arial", 48)
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x200")
self.window.title("Test app")
# Create a text label
self.question_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="What is your name?")
self.question_label.place(x=20, y=20)
# Create a text entry box
self.name_entry = tk.Entry(self.window)
self.name_entry.place(x=20, y=50)
self.name_entry.focus() # Put the cursor in the text box
# Create a button
self.submit_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Submit", command=self.greetings)
self.submit_button.place(x=20, y=100)
# Create a second button
self.close_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Close", command=self.window.quit)
self.close_button.place(x=120, y=100)
def greetings(self):
# This function is executed when the submit button is clicked
# Retrieve the text from the entry box
person = self.name_entry.get()
# Display a message box
messagebox.showinfo("Greetings", f"Hello {person}, welcome to Tkinter!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Example 3: Listbox, simpledialog
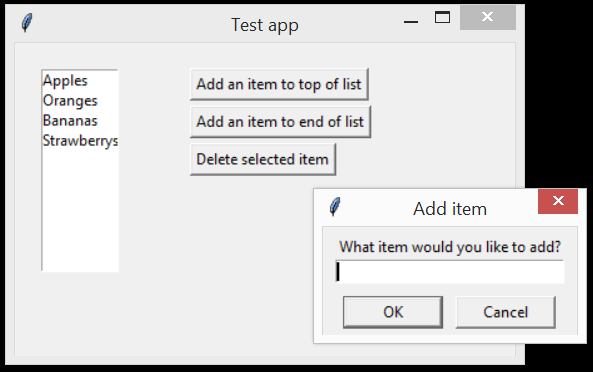
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import messagebox
from tkinter import simpledialog
# Pre-define some defaults
FONT_LARGE = ("Arial", 48)
# List of items to demo listbox
items = ["Apples", "Oranges", "Bananas", "Strawberrys"]
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x250")
self.window.title("Test app")
# Create a list box
# -- width is characters, height is lines
self.list = tk.Listbox(self.window, width=10, height=10)
for item in items:
# Add each item to the end of the list
self.list.insert(tk.END, item)
self.list.place(x=20, y=20)
# -- When an item in the list is selected, execute the list_clicked function
self.list.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', self.list_clicked)
# -- Give `selected` a default of -1
self.selected = -1
# Create some buttons
self.add_to_top_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Add an item to top of list", command=self.add_to_top_clicked)
self.add_to_top_button.place(x=140, y=20)
self.add_to_end_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Add an item to end of list", command=self.add_to_end_clicked)
self.add_to_end_button.place(x=140, y=50)
self.close_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Delete selected item", command=self.delete_selected_clicked)
self.close_button.place(x=140, y=80)
def add_to_top_clicked(self):
answer = simpledialog.askstring("Add item","What item would you like to add?")
self.list.insert(0, answer)
def add_to_end_clicked(self):
answer = simpledialog.askstring("Add item","What item would you like to add?")
self.list.insert(tk.END, answer)
def delete_selected_clicked(self):
if self.selected >= 0: # Check this still isn't -1
self.list.delete(self.selected)
self.selected = -1 # Reset back to -1
else:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Can't delete the selected item if you haven't selected anything!")
def list_clicked(self, e):
print(e)
self.selected = int(self.list.curselection()[0]) # item number selected in list
item = self.list.get(self.selected) # text of selected item
print(f"You have clicked item {self.selected} which is {item}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Example 4: Menubar, filedialog
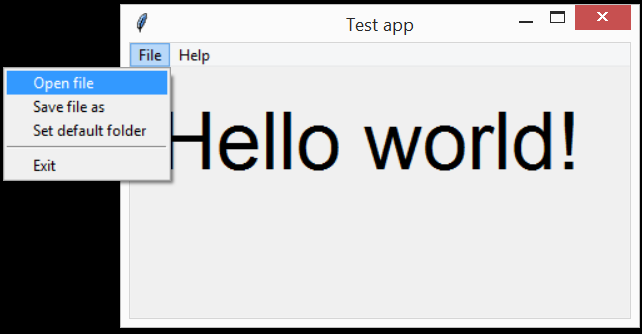
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import messagebox
from tkinter import filedialog
# Pre-define some defaults
FONT_LARGE = ("Arial", 48)
ALLOWED_FILES = (("JPEG files","*.jpg"),("PNG files","*.png"),("all files","*.*"))
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x200")
self.window.title("Test app")
# Create a text label and place it in the window
self.hello_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Hello world!", font=FONT_LARGE)
self.hello_label.place(x=20, y=20)
# Create a menu bar
menubar = tk.Menu(self.window)
filemenu = tk.Menu(menubar, tearoff=0)
filemenu.add_command(label="Open file", command=self.file_open)
filemenu.add_command(label="Save file as", command=self.file_saveas)
filemenu.add_command(label="Set default folder", command=self.select_folder)
filemenu.add_separator()
filemenu.add_command(label="Exit", command=self.window.quit)
helpmenu = tk.Menu(menubar, tearoff=0)
helpmenu.add_command(label="About", command=self.about)
menubar.add_cascade(label="File", menu=filemenu)
menubar.add_cascade(label="Help", menu=helpmenu)
self.window.config(menu=menubar)
# Intialise the default folder location
self.default_folder = "."
def file_open(self):
filename = filedialog.askopenfilename(initialdir=self.default_folder, title="Select file", filetypes=ALLOWED_FILES)
print(f"Open file: {filename}")
def file_saveas(self):
filename = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(initialdir=self.default_folder, title="Select file", filetypes=ALLOWED_FILES)
print(f"Save file as: {filename}")
def select_folder(self):
folder = filedialog.askdirectory(initialdir=self.default_folder, title = "Select folder containing student photos")
self.default_folder = folder
print(f"New default folder: {folder}")
def about(self):
messagebox.showinfo("About", "Copyright (c) 2019 Paul Baumgarten\nWebsite: pbaumgarten.com")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Example 5: Images
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
# Pre-define some defaults
FONT_LARGE = ("Arial", 48)
ALLOWED_FILES = (("JPEG files","*.jpg"),("PNG files","*.png"),("all files","*.*"))
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x400")
self.window.title("Test app")
# Button
self.pick_file_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Pick an image", command=self.show_image)
self.pick_file_button.place(x=20,y=20)
# Create a label reserved for displaying image later
self.image_label = tk.Label(self.window)
self.image_label.place(x=20,y=70,width=300,height=300)
def show_image(self):
# Get image selection
filename = filedialog.askopenfilename(title="Select image", filetypes=ALLOWED_FILES)
print(f"Opening file: {filename}")
# Open the image file
img = Image.open(filename)
# (optional) resize the image
img = img.resize((300, 300))
# 1. Reformat the image into tk compatible form, and
# 2. Save a copy of the image to self otherwise it will be cleared from memory when this function closes
self.tkimg = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
# Display the image in the label
self.image_label.configure(image=self.tkimg)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Example 6: Second window
To have Tkinter open second windows, use the tk.Toplevel() function as shown in the LoginWindow.__init__() function.
With respect to organising your code, it is generally good practice to make each window its own class.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import time
# Pre-define some defaults
FONT_LARGE = ("Arial", 48)
class LoginWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create a variable with which we can reference our parent
self.parent = parent
# Secondary windows are made using tk.Toplevel() instead of using parent
self.window = tk.Toplevel()
self.window.geometry("400x300")
self.window.title("Login")
# Labels
self.username_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Username:")
self.username_label.place(x=20,y=20)
self.password_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Password:")
self.password_label.place(x=20,y=70)
# Entry boxes
self.username_text = tk.Entry(self.window)
self.username_text.place(x=100,y=20)
self.username_text.focus()
self.password_text = tk.Entry(self.window, show="*")
self.password_text.place(x=100,y=70)
# Button
self.login_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Login", command=self.login)
self.login_button.place(x=100,y=120)
def login(self):
self.userid = self.username_text.get()
self.passwd = self.password_text.get()
print(f"Your username is {self.userid} and password is {self.passwd}")
# Close the login window
self.window.destroy()
def get_info(self):
return self.userid, self.passwd
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window (linked to the app parent)
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x200")
self.window.title("Test app")
# Create a text label and place it in the window
self.hello_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Hello world!", font=FONT_LARGE)
self.hello_label.place(x=20, y=20)
# Create a button
self.login_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Login", command=self.login_clicked)
self.login_button.place(x=20, y=170)
def login_clicked(self):
# Create login window
login_window = LoginWindow()
# Wait until the login window is closed
self.window.wait_window(login_window.window)
print("Finished waiting")
uid, pwd = login_window.get_info()
self.hello_label.configure(text=f"Hello {uid}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Example 7: Tabs
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import messagebox
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.window = parent
self.window.geometry("400x400")
self.window.title("Test app")
# Create a text label and place it in the window
self.hello_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Hello world!", font=FONT_LARGE)
self.hello_label.place(x=20, y=20)
# Create 3 tabs
self.tab_container = tk.Frame(self.window)
self.tab_container.place(x=0,y=0,width=400,height=400)
self.tabs = ttk.Notebook(self.tab_container)
self.tab_1 = tk.Frame(self.tabs)
self.tab_2 = tk.Frame(self.tabs)
self.tab_3 = tk.Frame(self.tabs)
self.tabs.add(self.tab_1, text="Tab 1")
self.tabs.add(self.tab_2, text="Tab 2")
self.tabs.add(self.tab_3, text="Tab 3")
self.tabs.place(x=0,y=0,height=400,width=400)
# Define what function to run when current tab is changed
self.tabs.bind("<<NotebookTabChanged>>", self.on_tab_selected)
# Content for tab 1
self.label1 = tk.Label(self.tab_1, text="I am the content of tab 1")
self.label1.place(x=20, y=20) # Coordinates are relative to within the tab area
# Content for tab 2
self.label2 = tk.Label(self.tab_2, text="I am the content of tab 2")
self.label2.place(x=20, y=20) # Coordinates are relative to within the tab area
# Content for tab 3
self.label3 = tk.Label(self.tab_3, text="I am the content of tab 3")
self.label3.place(x=20, y=20) # Coordinates are relative to within the tab area
self.close_button = tk.Button(self.tab_3, text="Close", command=self.close_clicked)
self.close_button.place(x=20,y=70)
def on_tab_selected(self, e):
# Function to execute whenever current tab is changed
selected_tab = e.widget.select()
tab_text = e.widget.tab(selected_tab, "text")
if tab_text == "Tab 1":
print("You clicked into tab 1")
if tab_text == "Tab 2":
print("You clicked into tab 2")
if tab_text == "Tab 3":
print("You clicked into tab 3")
def close_clicked(self):
result = messagebox.askyesno("Confirm", message="Do you want to quit?")
if result:
self.parent.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Demo project: Contacts app

This project can be found at https://github.com/paulbaumgarten/python-gui-contacts-app
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import messagebox
from tkinter import filedialog
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import os
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
contacts = [
{"phoneNumber":"555 0001","name":"Sheldon Lee Cooper","dateOfBirth":"1980-02-26","email":"sheldon@gmail.com"},
{"phoneNumber":"555 0002","name":"Howard Joel Wolowitz","dateOfBirth":"1981-03-01","email":"howard@gmail.com"},
{"phoneNumber":"555 0003","name":"Rajesh Ramayan Koothrappali","dateOfBirth":"1981-10-06","email":"raj@gmail.com"},
{"phoneNumber":"555 0004","name":"Penny Hofstadter","dateOfBirth":"1985-12-02","email":"penny@gmail.com"},
{"phoneNumber":"555 0005","name":"Amy Farrah Fowler","dateOfBirth":"1979-12-17","email":"amy@gmail.com"},
{"phoneNumber":"555 0002","name":"Bernadette Rostenkowski-Wolowitz","dateOfBirth":"1984-01-01","email":"bernadette@gmail.com"},
{"phoneNumber":"555 0006","name":"Leonard Hofstadter","dateOfBirth":"1980-05-17","email":"leonard@gmail.com"}
]
class AppWindow():
def __init__(self, parent):
# Create the window
self.parent = parent
self.window = tk.Toplevel()
self.window.geometry("670x350")
self.window.title("Contacts app")
self.window.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", self.window.quit)
# Create a text label and place it in the window
self.title_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Contacts app", font=("Arial", 16))
self.title_label.place(x=10, y=10)
# Create the list box
self.contact_list = tk.Listbox(self.window, width=25, height=17)
self.contact_list.place(x=10, y=40)
# -- When an item in the list is selected, execute the list_clicked function
self.contact_list.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', self.list_clicked)
self.update_list()
# Name
self.name_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Name", font=("Arial", 13))
self.name_label.place(x=250,y=40)
self.name_text = tk.Entry(self.window, width=25)
self.name_text.place(x=250,y=60)
# Email
self.email_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Email", font=("Arial", 13))
self.email_label.place(x=250,y=100)
self.email_text = tk.Entry(self.window, width=25)
self.email_text.place(x=250,y=120)
# Phone number
self.phone_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Phone", font=("Arial", 13))
self.phone_label.place(x=250,y=160)
self.phone_text = tk.Entry(self.window, width=25)
self.phone_text.place(x=250,y=180)
# Date of birth
self.dob_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Date of birth", font=("Arial", 13))
self.dob_label.place(x=250,y=160)
self.dob_text = tk.Entry(self.window, width=25)
self.dob_text.place(x=250,y=180)
# Age
self.age_label = tk.Label(self.window, text="Age", font=("Arial", 13))
self.age_label.place(x=250,y=220)
self.age_info = tk.Label(self.window, text="", font=("Arial", 13))
self.age_info.place(x=250,y=240)
# Photo
self.image_label = tk.Label(self.window)
self.image_label.place(x=500,y=40,width=150,height=200)
# Buttons
self.new_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Save new", command=self.save_new)
self.new_button.place(x=250, y=280, width=100, height=40)
self.existing_button = tk.Button(self.window, text="Save existing", command=self.save_existing)
self.existing_button.place(x=370, y=280, width=100, height=40)
def list_clicked(self, e):
self.selected = int(self.contact_list.curselection()[0]) # item number selected in list
print(f"You clicked item number {self.selected}")
# Get the selected contact
contact = contacts[self.selected]
# Show name
self.name_text.delete(0, tk.END)
self.name_text.insert(0, contact["name"])
# Show email
self.email_text.delete(0, tk.END)
self.email_text.insert(0, contact["email"])
# Show phone number
self.phone_text.delete(0, tk.END)
self.phone_text.insert(0, contact["phoneNumber"])
# Show date of birth and age
birthday = datetime.strptime(contact["dateOfBirth"], "%Y-%m-%d")
self.dob_text.delete(0, tk.END)
self.dob_text.insert(0, birthday.strftime("%d/%m/%Y"))
today = datetime.now()
age = today.year - birthday.year
if today.month < birthday.month:
age = age - 1
elif today.month == birthday.month and today.day < birthday.day:
age = age - 1
self.age_info["text"] = str(age) + " years"
# Show photo if it exists
if os.path.exists(contact["name"]+".jpg"):
img = Image.open(contact["name"]+".jpg")
img = img.resize((150, 200))
self.contact_photo = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
self.image_label.configure(image=self.contact_photo)
else:
self.contact_photo = None
self.image_label.configure(image=None)
def update_list(self):
# Empty list
self.contact_list.delete(0, tk.END)
# Add all contacts to list
for contact in contacts:
# Add each item to the end of the list
self.contact_list.insert(tk.END, contact["name"])
# Set a default to indicate no item selected
self.selected = -1
def save_new(self):
print("You clicked button save_new")
new_contact = {}
new_contact["name"] = self.name_text.get()
new_contact["email"] = self.email_text.get()
new_contact["phoneNumber"] = self.phone_text.get()
new_contact["dateOfBirth"] = datetime.strptime(self.dob_text.get(), "%d/%m/%Y").strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
contacts.append(new_contact)
self.update_list()
def save_existing(self):
print("You clicked button save_existing")
if self.selected >= 0:
contacts[self.selected]["name"] = self.name_text.get()
contacts[self.selected]["email"] = self.email_text.get()
contacts[self.selected]["phoneNumber"] = self.phone_text.get()
contacts[self.selected]["dateOfBirth"] = datetime.strptime(self.dob_text.get(), "%d/%m/%Y").strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
self.update_list()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
app = AppWindow(root)
root.mainloop()
Suggested resources
- https://python-textbok.readthedocs.io/en/1.0/Introduction_to_GUI_Programming.html
- http://www.effbot.org/tkinterbook/grid.htm
- https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/tkinter.html
- https://www.python-course.eu/python_tkinter.php